ECHO Technical Notes
ECHO Tech Notes are subject-specific publications about topics important to those working in the tropics and subtropics. Our material is authored by ECHO staff and outside writers, all with experience and knowledge of their subject. These documents are free for your use and will hopefully serve a valuable role in your working library of resources in agricultural development!
100 Matoleo katika Chapisho hili (Inaonyesha masuala 53 - 44) Iliyopita | Kifuatacho
Chaya - 01-01-2006
- Inapatikana pia katika:
- English (en)
- Français (fr)
- Español (es)
Dr. Martin Price, co-founder of ECHO and former head of ECHO’s Agricultural Resources Department, has said, “I would consider chaya to be one of the five most important underutilized food plants ECHO distributes. I give it this rank because of its ability to thrive in both arid and rainy regions, its little need for care or extra fertility, its lack of insect or disease pests, its high production per square foot, and the exceptional nutritional value of its cooked leaves.”
Frank Martin, Ruth Ruberté, and Laura Meitzner agreed; in their book Edible Leaves of the Tropics, they wrote, “As a year-round source of high-quality food in a wide range of conditions, it is one of the most important edible-leaved plants for the tropics.”
And in an article in Economic Botany 56(4), “The Ethnobotany of Chaya,” Jeffrey Ross-Ibarra and Alvaro Molina-Cruz concluded, “Its high nutritive value, ease of propagation, productivity, tolerance of poor growth conditions, and resistance to pests and disease all make chaya a valuable potential crop that could benefit peoples of many different regions.”
Moringa Water Treatment - 01-03-2005
- Inapatikana pia katika:
- Français (fr)
- English (en)
- Español (es)
In addition to food, shelter and clothing, water is one of our basic human needs and lack of potable water is a major cause of death and disease in our world. The purpose of this document is to provide information on household water treatment using seeds of the Moringa oleifera tree.
Using natural materials to clarify water is a technique that has been practiced for centuries and of all the materials that have been used, seeds of the Moringa have been found to be one of the most effective.
Moringa Leaf Powder - 20-01-2005
- Inapatikana pia katika:
- Français (fr)
- Español (es)
- Kreyòl Ayisyen (ht)
- English (en)
The leaves of the Moringa oleifera tree are very nutritious. They can be consumed fresh, cooked or dried. Since dried Moringa leaves retain their nutrient content, it is possible to convert them into leaf powder. When there is an abundance of leaves, this leaf powder can be made and stored easily. Moringa Leaf Powder is an excellent nutritional supplement and can be added to any dish.
Statistical Analysis of Simple Agricultural Experiments - 01-04-2003
Use of a new crop variety or production technique may dramatically increase food production in a given area. Alternatively, an innovation successful in North America may utterly fail in the tropics. The goal of “adaptive research” is to evaluate a particular innovation for its usefulness under local conditions. This technical note is written for those who want to improve the quality of their experiments but who have little or no background in statistics. It supplements the 81st issue of ECHO Development Notes with step-by-step instructions on how to manually calculate statistics for the most commonly used experimental designs. A little persistence, very basic math skills, and perhaps a calculator are all you need to do the calculations. If you have a computer equipped with statistical software, doing a set of calculations by hand or with a calculator will help you to understand how to use the software and interpret the output. Examples are given for experiments in which only one factor (e.g. crop variety) is tested. A limited amount of statistical terminology is woven into the text for the benefit of those interested in further study.
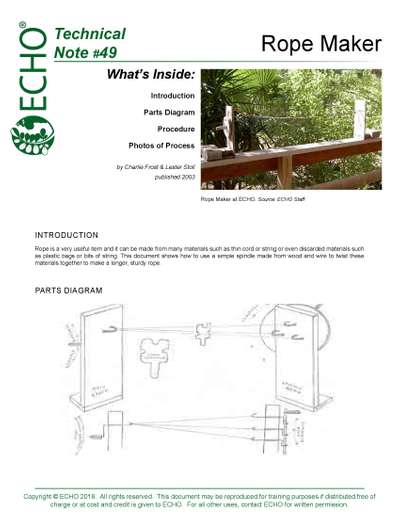
Rope Maker - 01-01-2003
Rope can be made from cord or string or even discarded plastic bags using a simple spindle to twist the materials together.
Acid Soils of the Tropics - 01-01-2002
- Inapatikana pia katika:
- Français (fr)
- English (en)
Acidification of soil is a natural process with major ramifications on plant growth. As soils become more acid, particularly when the pH drops below 4.5, it becomes increasingly difficult to produce food crops. As soil pH declines, the supply of most plant nutrients decreases while aluminum and a few micronutrients become more soluble and toxic to plants. These problems are particularly acute in humid tropical regions that have been highly weathered. According to Sanchez and Logan (1992), for example, one third of the tropics, or 1.7 billion hectares, is acid enough for soluble aluminum to be toxic for most crop plants. We will look at some of the causes of acidification and list some of the expected results of both acidification and the practice of liming for acid neutralization.
What’s Inside:
- What Causes Soil to Become Acid?
- Soil pH and Aluminum
- Effects of Acidification
- Solution to the Problem
- What Happens When Soil is Limed
- Dangers of Over-Liming the Soil
Composting Toilets - 01-01-2002
A composting toilet is any system that converts human waste into compost through the natural breakdown of organic matter. The photo above shows a composting toilet from the late 1800’s. Composting toilets provide a sanitary method to recycle human waste while conserving water and protecting the environment. In addition, they produce a valuable fertilizer. Composting toilets can be divided into batch systems and continuous use systems. The models covered here are batch systems.
Papaya Leaf Tea as a Malaria Prophylactic? - 01-01-2002
ECHO does NOT recommend that anyone stop taking their antimalarial medicine in order to try this treatment. The only evidence for the effectiveness of papaya leaf tea in the prevention of malaria is anecdotal. No studies have been done to scientifically demonstrate its effectiveness.
Does papaya leaf tea prevent malaria? In ECHO Development Notes Issue 69 (September 2000), we asked if any of those in our network had heard of the use of papaya leaf tea for the treatment and/or prevention of malaria. We were prompted by a question from two development workers in Indonesia who wrote to ECHO inquiring whether papaya leaves contained quinine. They wondered because tea from the leaves is widely used there in the belief that it prevents malaria. Dr. Rolf Myhrman at Judson College analyzed the bitter leaves for quinine, but found none. That does not, of course, rule out the possibility that some other chemical in the leaves may be effective.
Should an Institution Grow its Own Food - 01-06-2001
Several times each year ECHO hears from someone (1) at an institution that is evaluating whether it should attempt to grow food for its [students, orphans, feeding program, staff, etc.] or (2) from someone contacted by such an institution and are asking ECHO's advice about whether/how to help them. Usually the institution has land that they could be farming or the government has promised to give it to them.
Methane Digester - 01-01-2001
- Inapatikana pia katika:
- Español (es)
- Français (fr)
- English (en)
When organic material decomposes under anaerobic conditions, it produces biogas which is a mixture of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) with small quantities of hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon monoxide and other compounds. Biogas can be used as a fuel source for cooking, heating, producing light or even fueling a generator. A methane digester is a device used to produce and capture this biogas. There are many designs for methane digesters ranging from large and complex to small and simple. This document will cover 2 main types of digesters: batch digesters and flow-thru digesters; and 2 main types of gas collectors: tube collectors and floating collectors.